You will often see galvanized steel sheet as the top choice for construction and outdoor projects because it resists rust and lasts longer in harsh environments. For precision manufacturing, you might prefer cold-rolled steel for its smooth finish and strength. When you decide, look at factors such as corrosion resistance, durability, cost, and your specific application needs. Recent industry data shows galvanized steel’s market value continues to rise, especially in automotive body parts, while cold-rolled steel grows steadily due to its formability and strength. Always consider your project’s environment and industry standards before you choose.
Key Takeaways
- Galvanized steel sheet is ideal for outdoor projects due to its excellent corrosion resistance and long lifespan.
- Cold-rolled steel offers a smooth finish and high strength, making it perfect for precision manufacturing and automotive interiors.
- Consider the environment of your project; galvanized steel performs better in humid or coastal areas, while cold-rolled steel is suited for controlled indoor settings.
- Cost is an important factor; galvanized steel typically has a lower initial cost and requires less maintenance over time.
- Choose galvanized steel for construction applications like roofing and structural components, where durability is crucial.
- Select cold-rolled steel for applications needing tight tolerances and a polished appearance, such as furniture and appliances.
- Evaluate your project’s specific needs, including strength, corrosion resistance, and budget, to make the best steel choice.
- Consult industry experts to align your material selection with project goals and ensure optimal performance.
Comparison Overview
Key Differences
When you compare galvanized steel and cold-rolled steel, you notice several important differences. Each type offers unique benefits for your project. The table below summarizes the main distinctions in corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, cost, and typical applications.
| Criteria | Cold-Rolled Steel | Galvanized Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resistant to rust in humid and coastal environments | Moderate, prone to rust in humid conditions |
| Mechanical Strength | High, suitable for precision parts | Strong, ideal for structural and outdoor uses |
| Cost | Higher due to complex manufacturing | Lower, suitable for larger projects |
| Typical Applications | Automotive interiors, furniture, appliances | Construction, automotive body parts, roofing, appliances |
You see that cold-rolled steel provides a smooth surface and high strength. It works well for parts that need tight tolerances and a clean finish. Galvanized steel stands out for its protective zinc coating, which improves durability and extends service life. You benefit from its lower cost when you need large quantities for construction or outdoor projects. If your project requires high corrosion resistance, cold-rolled steel performs better in humid or coastal environments.
Best Uses
You should choose your steel type based on your industry and project needs. Different sectors rely on each material for specific reasons.
- The automotive industry has increased its use of galvanized steel by 22% over the past five years. You see this material in body shells, chassis, and fuel tanks.
- The construction sector accounts for about 40% of galvanized steel demand. You find it in roofing, doors, windows, and structural components.
- Cold-rolled steel remains popular in manufacturing, especially for furniture and appliance production. The construction industry also uses cold-rolled steel, making up 35% of its demand.
Tip: If you work in construction or automotive manufacturing, galvanized steel often meets your needs for durability and cost-effectiveness. For projects that require a flawless surface or precise dimensions, cold-rolled steel is the better choice.
You should always consider your environment, budget, and required mechanical properties before making a decision. Galvanized steel offers reliable performance for outdoor and structural applications. Cold-rolled steel excels in projects where appearance and precision matter most.
Galvanized Steel Sheet
Definition
You use galvanized steel sheet when you need steel that resists rust and lasts for years. Manufacturers create this material by dipping steel into molten zinc at high temperatures. The zinc forms a protective layer that shields the steel from moisture and oxygen. You can also find other galvanizing methods, such as the galvanic process, zinc spray, and Sherardization, but hot-dip galvanizing remains the most common for industrial use. WITOP’s Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheet stands out because it uses a continuous hot-dip process, ensuring a uniform zinc coating on both sides.
Properties
Corrosion Resistance
Galvanized steel sheet offers outstanding corrosion resistance. The zinc coating acts as a barrier, preventing rust and extending the life of the steel. You benefit from this protection in harsh environments, including coastal areas and industrial zones. Engineering standards show that galvanized steel sheet can last over 50 years in moderate conditions and more than 20 years in severe climates. Once installed, you do not need to perform additional maintenance, which saves you time and money.
Mechanical Strength
You rely on galvanized steel sheet for its high mechanical strength. Metallurgical studies reveal that it provides higher yield and tensile strength compared to other steel types. WITOP’s Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheet delivers yield strengths from 300 to 400 MPa and tensile strengths between 300 and 550 MPa. You can select from soft, semi-hard, or full hard options to match your project’s requirements. The sheet’s strength makes it suitable for rolling, stamping, and bending in various manufacturing processes.
Cost
Galvanized steel sheet gives you excellent value. The initial investment is lower than many other steel products, especially when you need large quantities for construction or manufacturing. You also save on long-term costs because the material requires no maintenance and resists damage from the environment. WITOP ensures quality by testing every sheet for thickness, zinc coating, and hardness, so you receive reliable performance with every order.
Applications
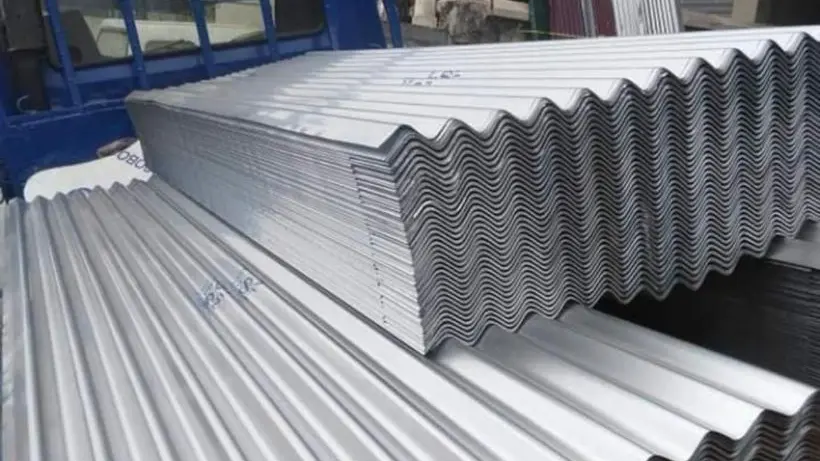
Construction
You see galvanized steel sheet used in roofs, doors, windows, and ceiling keels. Its durability and corrosion resistance make it ideal for outdoor structures and building frameworks.
Automotive
Automotive manufacturers rely on galvanized steel sheet for body shells, chassis, and fuel tanks. The zinc coating prevents rust and increases the lifespan of vehicles.
Appliances
You find galvanized steel sheet in refrigerators, washing machines, and other home appliances. The material’s strength and attractive finish help create reliable and appealing products.
Metallurgy
Galvanized steel sheet plays a key role in producing steel window blanks and substrates for color-coated boards. Its versatility supports a wide range of metallurgical applications.
Tip: WITOP’s Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheet comes in multiple spangle options, including zero, small, regular, and big spangle, allowing you to choose the best look for your project.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Rust Resilience | Zinc provides a protective barrier to the steel, creating a defense against oxygen and moisture. |
| Extended Life Span | Galvanized sheets can last over 50 years in moderate environments and over 20 years in severe conditions. |
| No Maintenance Required | Once galvanized, no further maintenance is needed. |
| Easy Inspection | You can assess the strength visually and test the zinc layer thickness with standard methods. |
Cold-Rolled Steel

Definition
You choose cold-rolled steel when you need precision and a flawless surface. Manufacturers produce this material by rolling steel at room temperature after the initial hot rolling stage. The cold-rolling process compresses the steel between rollers, which refines its thickness and improves its mechanical properties. This method creates a product with tight dimensional tolerances and a clean, polished appearance.
The mechanical properties of dual-phase steel are significantly influenced by the ferrite-to-martensite ratio and grain size. Increasing the fraction of the reinforcing phase enhances yield and tensile strength, although it may reduce elongation. The manufacturing process involves thermomechanical treatment, which alters the microstructure and improves the overall mechanical properties of the steel.
Properties
Surface Finish
Cold-rolled steel stands out for its smooth and uniform surface. You benefit from a material that looks polished and feels clean to the touch. The process aligns the grain structure, which reduces imperfections and creates a pristine finish. This quality makes cold-rolled steel ideal for products where appearance matters, such as appliance panels and furniture.
- Cold-rolled steel offers higher dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for precision engineering and manufacturing where tight tolerances are essential.
- The process results in a smoother, polished surface finish, which is advantageous for applications needing a pristine appearance.
- Cold rolling aligns the grain structure of the steel, enhancing its strength and resistance to deformation, beneficial for materials under tension.
Strength
You rely on cold-rolled steel for its superior strength. The rolling process at lower temperatures increases the hardness and durability of the steel. You get a product that is about 20% stronger than hot-rolled steel. This added strength allows you to use cold-rolled steel in high-stress environments, including automotive components and structural frameworks.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Yield Strength | Decreases significantly when corrosion rate exceeds 15%. |
| Ultimate Strength | Also shows a notable reduction at higher corrosion rates, particularly above 20%. |
| Corrosion Impact | Corrosion leads to stress concentration and earlier structural damage. |
| Surface Morphology | Characterized by parameters like maximum corrosion depth and roughness, affecting mechanical properties. |
| Corrosion Measurement Methods | Includes mass loss rate and advanced techniques like SEM and AFM for detailed analysis. |
Cost
Cold-rolled steel usually costs more than hot-rolled steel because of the extra processing steps. You pay for the improved surface quality and higher precision. The investment pays off when you need parts that fit together perfectly or require minimal finishing. You also save time in manufacturing since cold-rolled steel often needs less secondary processing.
Applications
Manufacturing
You use cold-rolled steel in manufacturing when you need strong, smooth, and precise components. This material is essential for creating tools, machines, and frameworks that last longer and perform reliably.
| Application Area | Evidence of Suitability |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Strong, smooth, and precise, these bars are essential for creating quality tools and machines that last longer. |
Automotive (Interior)
Automotive manufacturers choose cold-rolled steel for interior parts that demand a flawless finish and tight tolerances. You find it in drive shafts, axles, and other components that must withstand constant stress while maintaining a refined look.
| Application Area | Evidence of Suitability |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Used in drive shafts and axles, cold rolled steel bars provide the necessary toughness to withstand constant stress. |
Furniture
You select cold-rolled steel for furniture frames and decorative pieces. The smooth surface and consistent dimensions allow you to create products that look attractive and fit together perfectly. This material supports modern design trends and ensures durability in everyday use.
- Cold-rolled steel undergoes additional processing after hot rolling, which enhances its quality and performance. The cold rolling process not only improves the surface finish but also increases the strength and durability of the steel, making it suitable for high-stress applications. The resulting material is characterized by a cleaner surface that is less prone to corrosion, and its dimensional consistency allows for the production of components that require minimal secondary processing.
Tip: You should consider cold-rolled steel for projects where appearance, strength, and precision are top priorities. Its corrosion resistance and dimensional accuracy make it a preferred choice in many industries.
Galvanized Steel vs Cold-Rolled Steel
Durability
When you compare the durability of galvanized steel and cold-rolled steel, you see clear differences in how each material performs over time. Galvanized steel stands out for its ability to withstand harsh environments. The zinc coating acts as a shield, protecting the steel from moisture, oxygen, and industrial pollutants. In moderate environments, you can expect galvanized steel to last between 20 and 50 years. If you use it in rural settings, the lifespan often exceeds 75 years. This level of durability makes it a preferred choice for outdoor structures and construction projects.
Cold-rolled steel offers good durability in controlled indoor environments. However, it does not match the longevity of galvanized steel when exposed to corrosive elements. You may find cold-rolled steel suitable for furniture, appliance panels, and automotive interiors, but its durability decreases in humid or coastal areas.
Note: Environmental factors such as salt exposure, humidity, and temperature play a major role in determining the durability of steel products. Always assess your project’s location before selecting a material.
| Steel Type | Corrosion Resistance | Lifespan in Moderate Environments | Lifespan in Rural Settings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galvanized Steel | Superior | 20-50 years | Over 75 years | Not suitable for high temperatures and alkaline environments |
| Cold-Rolled Steel | Good | Less durable | Varies | Limited size and thickness (usually < 4mm) |
You can see from the table that galvanized steel provides unmatched durability for most outdoor and industrial applications. Cold-rolled steel works best where environmental exposure is minimal.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a key factor in determining the durability of steel products. Galvanized steel excels in this area due to its zinc coating. You benefit from lower rates of red rust formation and superior performance in salt-spray and cyclic tests. The zinc layer also helps prevent scribe creep and perforation, which are common issues in steel exposed to moisture.
- Galvanized steel shows significantly better corrosion resistance than cold-rolled steel in standardized tests.
- Lower rates of red rust formation are observed in galvanized steel.
- Galvanized steel exhibits superior performance in scribe creep and perforation resistance.
Cold-rolled steel, while strong and precise, does not offer the same level of corrosion protection. You may need to apply additional coatings or treatments if you use cold-rolled steel in environments with high humidity or salt exposure.
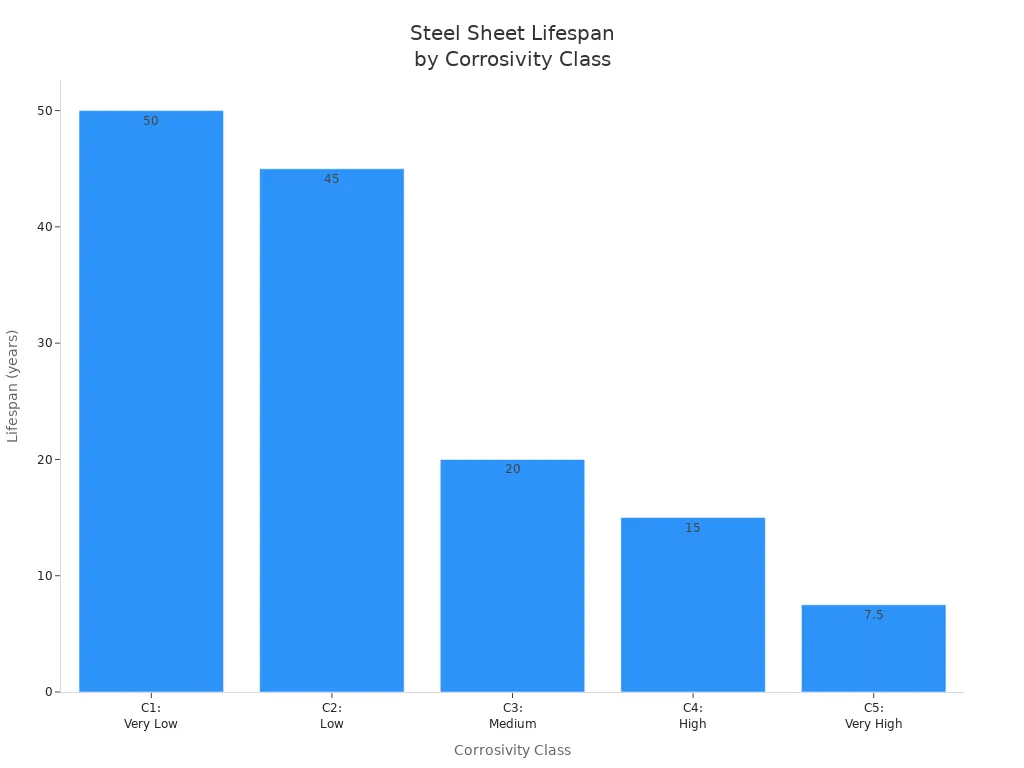
The chart above illustrates how the durability of galvanized steel varies across different corrosivity classes. In very low corrosivity environments, you can expect a lifespan of over 50 years. In high corrosivity areas, the lifespan drops to 10-20 years, but it still outperforms cold-rolled steel in similar conditions.
Cost
Cost is another important consideration when you choose between galvanized steel and cold-rolled steel. Galvanized steel typically has a lower initial material cost, especially when you need large quantities for construction or manufacturing. You also save on maintenance expenses because the zinc coating reduces the need for frequent repairs.
- Initial material cost for galvanized steel is lower than cold-rolled steel.
- Galvanized steel requires less maintenance due to its corrosion resistance.
- Cold-rolled steel may incur higher maintenance costs in harsh environments.
If you prioritize durability and long-term savings, galvanized steel offers excellent value. Cold-rolled steel may have a higher upfront cost, but it provides a smooth finish and precise dimensions, which are valuable in specialized manufacturing.
Tip: For projects where durability and cost-effectiveness matter most, galvanized steel is often the better choice. If your application demands a flawless surface and tight tolerances, cold-rolled steel may justify the extra investment.
Industry Suitability
Construction
You often face tough decisions when choosing steel for construction projects. Galvanized steel gives you a strong advantage in this industry. You get reliable protection against rust, which is essential for roofs, doors, and window frames. The zinc coating on galvanized steel helps your structures last longer, even in wet or coastal environments. You can use galvanized steel for ceiling keels and wall studs, which means your buildings stay sturdy and safe for years.
Many construction professionals prefer galvanized steel because it offers a balance of strength and cost-effectiveness. You save money on maintenance since the zinc layer prevents corrosion. When you need to meet building codes and safety standards, galvanized steel helps you achieve compliance with ease.
Tip: You should choose galvanized steel for outdoor structures and areas exposed to moisture. This choice reduces long-term repair costs and increases the lifespan of your projects.
Automotive
You see galvanized steel as a key material in the automotive industry. Car manufacturers use galvanized steel for body shells, chassis, and fuel tanks. The zinc coating protects vehicles from rust, which is critical for safety and durability. You benefit from fewer repairs and longer-lasting vehicles when you select galvanized steel for exterior parts.
Inside the vehicle, you might use cold-rolled steel for interior panels and decorative trim. Cold-rolled steel provides a smooth finish and precise dimensions, which are important for visible components. However, for parts exposed to the elements, galvanized steel remains the top choice.
Automotive engineers also rely on other steel types, such as high-end alloy steel and low-alloy high-strength tempered steel, for critical components. These steels offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and toughness. Still, galvanized steel stands out for its corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness in mass production.
Manufacturing
You work in manufacturing where both galvanized and cold-rolled steel play important roles. Galvanized steel is ideal for products that need to resist rust, such as appliance housings, metal cabinets, and industrial shelving. You can stamp, bend, and roll galvanized steel without losing its protective qualities. This versatility makes it a favorite for high-volume production.
Cold-rolled steel excels in manufacturing applications that demand tight tolerances and a flawless surface. You use cold-rolled steel for precision tools, furniture frames, and machine parts. Tool steel and carbon steel also appear in manufacturing, offering hardness and durability for specialized equipment.
The table below summarizes how different steel types fit into major industries:
| Steel Type | Industry Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| galvanized | Construction, Automotive, Manufacturing | Corrosion resistance, durability, cost-effectiveness, versatility |
| High-end alloy steel | Automotive, Construction | Superior strength-to-weight ratios, ideal for critical applications |
| Low-alloy high-strength tempered steel | Automotive, Construction | Exceptional mechanical properties, strength, and toughness |
| Carbon steel | Automotive, Manufacturing, Construction | High tensile strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness |
| Stainless steel | Automotive, Aerospace, Construction | Corrosion resistance, strength, and aesthetic appeal |
| Tool steel | Manufacturing | Hardness, resistance to abrasion, and ability to retain a cutting edge |
Note: You should match your steel choice to your project’s requirements. Galvanized steel works best for outdoor and high-moisture environments. Cold-rolled steel fits projects where appearance and precision matter most.
Choosing the Right Steel
Decision Factors
Selecting the right steel for your project requires careful evaluation of several factors. You need to match the material’s properties to your application’s demands. The following table summarizes the most important decision points when comparing galvanized steel and cold-rolled steel:
| Factor | Galvanized Steel | Cold-Rolled Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High due to zinc coating | Requires coatings to prevent rust |
| Mechanical Properties | Good durability and low maintenance | Higher tensile strength, more wear-resistant |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost but lower maintenance | Lower initial cost but may incur higher maintenance costs |
Environment
You must consider the environment where you will use the steel. Galvanized steel performs best in outdoor or industrial settings. The zinc coating from the galvanizing process provides a self-healing barrier, which means even if the surface gets scratched, the underlying steel remains protected. This feature gives you high durability and resistance to moisture, humidity, and extreme weather. In freshwater, a protective layer forms on the surface, reducing corrosion rates. In contrast, cold-rolled steel needs additional coatings to resist rust, especially in humid or coastal areas.
- Corrosion rates in pure water can vary, but hard water slows down corrosion by forming protective scales.
- Galvanized steel adapts well to changing weather and water exposure, making it ideal for construction and infrastructure.
Strength Needs
You should assess the mechanical requirements of your project. Cold-rolled steel offers higher tensile strength and better wear resistance, which makes it suitable for applications that demand precision and durability. If your project involves heavy loads or moving parts, you may prefer cold-rolled steel for its strength. However, galvanized steel provides good durability and low maintenance, which is essential for structures exposed to the elements.
- Galvanized steel’s high durability ensures a longer lifespan for outdoor structures.
- Cold-rolled steel excels in applications where strength and dimensional accuracy are critical.
Budget
Budget plays a significant role in your decision. Galvanized steel may have a higher initial cost due to the zinc coating, but you save money over time because of its low maintenance needs. Cold-rolled steel often costs less upfront, but you might face higher maintenance expenses if you use it in corrosive environments. Always factor in both the purchase price and the long-term costs when making your choice.
Tip: Understanding the unique properties of each material helps you avoid costly mistakes and ensures your project lasts.
Industry Recommendations
Construction
For construction projects, you need materials that offer high durability and resistance to corrosion. Galvanized steel stands out in this sector. You can use it for roofs, wall cladding, doors, and window frames. The zinc coating ensures your structures withstand harsh weather and require minimal upkeep. WITOP provides several product options, such as galvanized plain sheets for ducting and wall cladding, and galvanised flat sheets for custom fabrication. These products meet industry standards like EN, ASTM, and JIS, ensuring compliance and quality.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, you must balance strength, resistance, and cost. Galvanized steel is the preferred choice for body shells, chassis, and fuel tanks because it resists rust and delivers high durability. The self-healing zinc layer protects vehicles from moisture and road salts, extending their service life. For interior components that require a flawless finish and precise dimensions, cold-rolled steel is often used. WITOP’s galvannealed steel sheet, with its matte surface, is valued for paintability and weldability in automotive applications.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing demands materials that combine strength, resistance, and versatility. You often use galvanized steel for appliance housings, metal cabinets, and industrial shelving. Its high durability and low maintenance make it ideal for high-volume production. Cold-rolled steel is your go-to for precision tools, furniture frames, and machine parts where tight tolerances matter. Tool steel and carbon steel also play roles in manufacturing, offering hardness and long-lasting performance.
Appliances
When producing appliances, you need steel that offers both strength and a clean appearance. Galvanized steel provides the corrosion resistance required for refrigerators, washing machines, and other home appliances. The zinc coating ensures a longer lifespan and keeps products looking new. Cold-rolled steel is also common in appliance panels, where its smooth surface and high strength are essential. WITOP’s galvanized zinc sheet and galvannealed steel sheet meet the demands of modern appliance manufacturing, offering both durability and aesthetic appeal.
Note: Always check for industry certifications and standards, such as DX51D or ASTM A653M, to ensure your steel meets project requirements. WITOP’s products undergo third-party testing for compliance, giving you confidence in every order.
By carefully considering your environment, strength needs, and budget, you can select the steel that best fits your industry. WITOP’s range of galvanized steel sheets provides solutions for construction, automotive, manufacturing, and appliance sectors, helping you achieve high durability and a longer lifespan for your projects.
You see clear differences between galvanized steel sheet and cold-rolled steel. Galvanized steel works best for construction and outdoor projects because it resists corrosion and offers long-term durability. Cold-rolled steel suits manufacturing and automotive interiors where precision and surface finish matter most.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Strength and Durability | High-strength steel is essential for structural applications. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Stainless and galvanized steel are ideal for environments with moisture exposure. |
| Machinability | Some steel grades are easier to cut, weld, and shape. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Balancing quality and budget is crucial in large-scale projects. |
You should consult with industry experts to optimize your steel selection. Professionals help you align materials with your project goals and identify risks. Choose the right steel for your next project to ensure lasting performance and value.
FAQ
What is the main difference between galvanized steel sheet and cold-rolled steel?
You get galvanized steel sheet with a zinc coating for corrosion resistance. Cold-rolled steel offers a smooth finish and higher precision. You should choose based on your need for durability or appearance.
Can you use galvanized steel sheet for indoor projects?
Yes, you can use galvanized steel sheet indoors. It provides extra protection against moisture and accidental spills. You often see it in ductwork, appliance housings, and wall panels.
Which steel type is better for outdoor construction?
You should select galvanized steel sheet for outdoor construction. The zinc coating protects against rain, humidity, and harsh weather. This choice helps your structures last longer with less maintenance.
Does cold-rolled steel rust easily?
Cold-rolled steel can rust if exposed to moisture or corrosive environments. You need to apply protective coatings or paint for long-term use, especially in humid or coastal areas.
How do you choose the right steel for your project?
You should consider your environment, strength needs, and budget. For outdoor or high-moisture areas, pick galvanized steel. For projects needing a flawless finish or tight tolerances, choose cold-rolled steel.
What industries use galvanized steel sheet the most?
You find galvanized steel sheet widely used in construction, automotive, appliances, and metallurgy. These industries value its corrosion resistance, strength, and cost-effectiveness.
Can you weld or paint galvanized steel sheet?
Yes, you can weld or paint galvanized steel sheet. You need to follow proper procedures to avoid damaging the zinc coating. Always use suitable primers and welding techniques for best results.
Is galvanized steel sheet more expensive than cold-rolled steel?
You usually pay less for galvanized steel sheet when buying in large quantities. Cold-rolled steel costs more due to extra processing. Your total cost depends on your project size and requirements.